1. Creating
Physical Architecture
Physical Architecture
a. The
physical architecture defines the different elements of the information system,
as well as their characteristics taken into account by Oracle Data Integrator
b. Each
type of database (Oracle, DB2, etc.) or file format (XML, Flat File), or
application software is represented in Oracle Data Integrator by a technology
c. The
physical components that store and expose structured data are defined as
"Data Server"
d. A
data server is always linked to a single technology. A data server stores
information according to a specific technical logic which is declared into
physical schemas attached to this data server
Process to create
Physical Architecture:
Data Server:
i.
Open ODI Studio
ii.
Connect to Master repository with
Supervisor Privileges
iii.
Go to Topology Navigator
iv.
Expand Technologies and select Oracle
Technology
v.
Right click on it, select New Dataserver
vi.
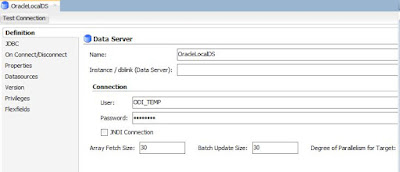
In the Definition mention as per below
screenshot
Name:
OracleLocalDS
User:
ODI_TEMP
Password:
Password
vii.
In the JDBC tab mention as per below
screenshot
JDBC
Drive: Select “oracle.jdbc.OracleDriver”
JDBC
URL: jdbc:oracle:thin:@<host>:<port>:<sid>
viii.
Click on Test Connection – Click Test –
click Ok
ix.
Hence Data server creation Completed
Physical Schema:
i.
Right click on Data Server (i.e.,OracleLocalDS)
ii.
Select New Physical schema
iii.
Enter details as mentioned below
Schema (Schema) – Data Schema à
ODI where inserts and updates target tables
Schema (Work Schema) – Work Schema à
Schema where all temporary tables (E$_,C$_...) are created and dropped by ODI
iv.
Click on Save – Click on Ok
2. Creating
Context
Context:
Contexts bring together
components of the physical architecture (the real Architecture) of the information
system with components of the Oracle Data Integrator logical architecture (the
Architecture on which the user works)
Process to Create:
i.
Go to Topology navigator
ii.
Expand Context Accordion
iii.
Click on the New Context
Name:
Context Name
Code:
Unique among various Repositories
v.
Click on Save
3. Creating
Logical Architecture
Logical Architecture:
a. The
logical architecture allows a user to identify as a single Logical Schema a
group of similar physical schemas - that is containing data stores that are
structurally identical - but located in different physical locations
b. Logical
Schemas, like their physical counterpart, are attached to a technology
c. All
the components developed in Oracle Data Integrator are designed on top of the
logical architecture. For example, a data model is always attached to logical
Schema
Process to Create Logical Architecture:
i. Go
to Topology Navigator
ii. Expand Logical Architecture
iii.
Expand Technologies and right click on Oracle Technology
Click on New Logical Schema
Select Physical Schema for context
Click on Save



No comments:
Post a Comment